Design guidelines for cylindrical joints
According to VDI 2230 guidelines.
| Cylindrical joints | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Item | Guidelines for design | Disadvantages | Advantages |
| 1 | Preloads: Preloads as high as possible *Higher strength grade *Exact tightening method *Low coefficients of friction | Low preloads | High preloads (choose tightening method with small tightening factor) |
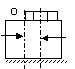
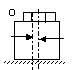
| 2 | Eccentricity of the bolt: Aim to obtain the lowest possible eccentricity of bolt positions |
Large eccentricity
 |
Minimal eccentricity
 |
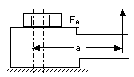
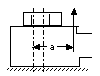
| 3 | Eccentricity of the load introduction: Minimal eccentricity causes smaller additional bolt forces |
Large eccentricity
 |
Minimal eccentricity
 |
| 4 | Height of load introduction: Introduce the load as close to the interface as possible |
Load introduction of the upper region
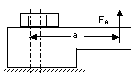 |
Load introduction in the vicinity of the interface
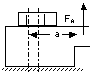 |
| 5 | Rigidity bolt - cylinder: The resilience of the bolt should be as high as possible, compared to the resilience of the clamped part. If need be, with reduced body diameter bolts. |
Thin small cylinder (for given nominal diameter)
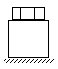 |
G = dW+hmin
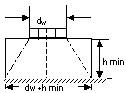 |